Quality Control department (QC)
OUR QUALITY VISION
Quality is embedded in everything we do.
As a producer, we are committed to high-quality products and services, manufacturing effectiveness, and meeting our customers’ expectations. meaning we provide quality, compliance and business support in the most effective and efficient way for the entire portfolio of our life science business.
OUR CAPABILITIES
Together with Operations, quality and regulatory professionals ensure compliance and high quality of our chemical products and services, Our product Quality & Regulatory Management team is responsible for identifying and mitigating risks with the support of a risk management system, and ensuring compliance with regulations related to:
• Chemicals
• Pharmaceutical
• Biologist
• Medical IVD
OUR QUALITY CULTURE
Quality Mission Statement is based on our company’s Quality Vision and demonstrates our commitment to quality. As the foundation of our Quality Culture, we have established the Quality Pyramid with its 5 Behavioral Elements and their respective Excellence Criteria.
We foster a quality culture based on:
• Highly qualified and proactive professionals
• An environment of customer centrality and continuous improvement
• Robust and standardized processes
• Integrated risk management and global tools
• Measurements aligned with customers’ expectations and regulatory needs.
OUR CODE OF CONDUCT
Several guidelines are part of our structured system of policies and help us to implement our values and principles. This system aims to ensure that all employees know the relevant rules and regulations, and can apply them to their work. Tried-and-proven management systems ensure that the processes relevant to our Corporate Responsibility strategy are systematically managed and monitored.
Everything we do is based on our 6 company values:
• Courage opens the door to the future
• Achievement makes our entrepreneurial success possible
• Responsibility determines our entrepreneurial actions
• Respect is the foundation of any partnership
• Integrity ensures our credibility
• Transparency makes mutual trust possible
Quality Control is one of the key departments in any Pharma company. After R&D large number of people works in the QC department. A chemist executing a qualitative analysis seeks to identify the substances in the sample. A quantitative analysis is an attempt to determine the quantity or concentration of a specific substance in the sample. For example, determining whether a sample of salt contains the element iodine is a qualitative analysis; measuring the percentage by weight of any iodine in the sample is a quantitative analysis.
Quality Control had two different divisions
Wet Analysis
Instrumental Analysis
The Quality will be checked in three different stages.
1) Raw material analysis
2) In Process Sample analysis
3) Finished Product analysis
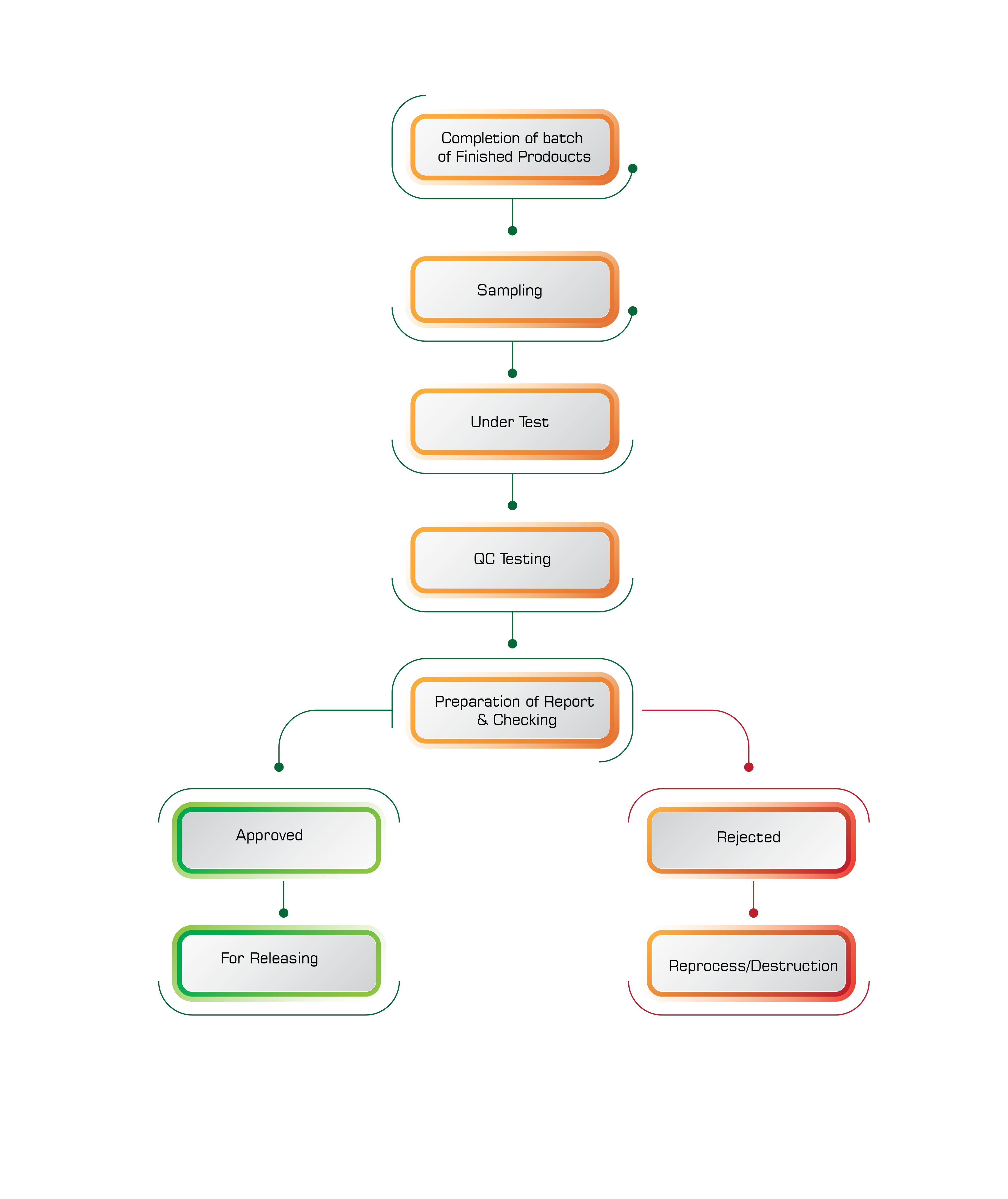
Once the raw material enters the factory premises and before going to the Stores department the Quality of the material will be checked by QC department. If the quality is as per the guidelines then the QC department approves the raw material. This is called Raw material analysis. The concerned QC chemist will perform the basic duties and the Group leader or Manager approves. The In Process Analysis will be done while the Product (Chemical or Formulation) is being Prepared/Manufactured Finished Product analysis will be done after the Product/material is manufactured.
The different Instruments used in QC department are:
HPLC
GC
UV
FTIR
AAS
KF Tritator
MV Tritator
Melting Point apparatus
Muffle Furnace
Polarimeter
Disentrigation Apparatus
TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography)
Water Bath
Dissolution apparatus
Before consuming any type of medicine, they need to be tested and approved for consumption in prepared pharmaceutical laboratories, so that they can be sold and consumed by the population. In this article, we will see in some topics how these processes work and their main function. The main objective of quality control in the Pharmaceutical Industry is to test the drugs in their various stages of production, verifying that they are able to proceed to the next stage and release the manufacturing process in accordance with the regulations and specifications required for consumption.
For complete control of the quality of the medication that is being produced, they need to be tested in several work areas. The main areas of research and analysis are:
• Physical-Chemical Laboratory
• Microbiological Laboratory
• Packaging Material Laboratory
• Process Control Laboratory
There are some necessary regulations so that there is a correct production and quality control of medicines. Each country has its rules and laws that govern these processes and each industry must follow and have the proper authorizations for production. To ensure that the rules and laws are being applied correctly, there are internal and external audits, aiming at the inspection of good medicine manufacturing practices. Analyzes are performed according to what each drug requires and depending on the phase this drug is in. In the physical-chemical laboratory, controls of all types are carried out, from the simplest to the most complex. We can mention as simple analyzes the product’s appearance, hardness, density and pH. As more complex, we can mention the most used method today in the largest pharmaceutical industries in the world, the content of the product (dosage), carried out in a device called HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography).
Each product goes through a production process and in a physico-chemical laboratory it is analyzed from the raw material, passing through the initial product, final product and stability study. Each phase requires special attention in its tests, following the literature established by the countries of dispatch and consumption of the drug. In Portugal, the European Pharmacopoeia is used as the main literature.
• Raw Material
Raw material means any substance, active or not, and whatever its origin, used in the production of medicine, whether it remains unchanged or changes or disappears during the process. Raw materials thus include excipients and active substances.
• Intermediate Product
Intermediate product is the partially processed mixture of the raw material with the necessary inputs in their due measures that must be subjected to subsequent manufacturing steps before becoming a bulk product.
• Bulk or Finished Product
Bulk or finished product is any product that has gone through all the stages of production of the medicine before the packaging process is completed. Sterile products in their primary packaging are considered bulk products.
• Stability
A stability study is the monitoring of each medication or pharmaceutical input from time to time to ensure that it maintains or does not lose a large percentage of its effectiveness. It is also carried out in the laboratory, as well as the other phases of the product, and can provide evidence on how these substances may vary over time from the influence of environmental factors such as temperature, light and humidity.
It is very important that each information, activity and deviation is properly registered and identified by the quality control. An unrecorded activity is seen as an unfulfilled activity.
Each person who works in quality control, must be qualified according to their area of expertise to perform their duties. Academic qualifications are extremely important, but there are also training courses for each function, equipment and rule applied in the sectors that the company must provide to employees. Quality control of the manufacture of medicines is essential to ensure that medicines are produced in the correct way and that they are fulfilling their main
Responsibilities of Quality Control (QC)
Along with safety and efficacy, quality is one of the most important criteria to assess the fitness of a medicinal product for use by the patient. This parameter is not something that can be achieved by itself, without any effort. While the earlier concept was to test products for quality, the pharmaceutical industry has now moved on to building quality into products right from the design stage itself. However, quality control (QC) still plays a vital role in giving a high degree of assurance that products are meeting their specifications.
Definition:
WHO, The World Health Organization defines the term quality control as, “The sum of all procedures undertaken to ensure the identity and purity of a particular pharmaceutical. Such procedures may range from the performance of simple chemical experiments which determine the identity and screening for the presence of a particular pharmaceutical substa,ce (thin layer chromatography, infrared spectroscopy, etc.), to more complicated requirements of pharmacopeial monographs.”
“Quality Control shall be concerned with sampling, specifications, testing, documentation, release procedures which ensure that the necessary and relevant tests are carried and that the materials are not released for use, nor products released for sale or supply until their quality has been judged to be satisfactory. It is not confined to laboratory operations but shall be involved in all decisions concerning the quality of the product. It shall be ensured that all quality control arrangements are effectively and reliably carried out the department as a whole shall have other duties such as to establish evaluate, validate and implement all Quality Control Procedures and methods.”
Scope of Quality Control:
Pharmaceutical QC aims at investigating manufactured drug products according to compendial specifications and standards to monitor that they are of the required quality. QC is concerned with setting up specifications, drawing samples, testing them, and generating documentation related to the tests and their reports. QC also evaluates the analysis reports and ensures that no material is released for use or supply or sale until it meets the necessary quality requirements and pre-determined specifications. The scope of QC is not limited to mere laboratory work; this department is involved in all situations that involve the quality of the product.
Organization of Quality Control:
Drug manufacturers are required to set up their QC labs and employ staff with the necessary qualifications and training to perform the necessary tests. The department must have adequate space to perform all the analyses, store data related to them, and also store reference samples from each batch of products shipped from the company.
Most quality control laboratories are divided into different types of testing – chemical, instrumental, biological, and microbiological.One of the fundamental requirements for the Quality Control department is that it must be independent of all the other departments. The Quality Control Head must report directly to the topmost authority, and not to the Production Head.
Responsibilities of Quality Control:
Responsibilities of quality control are as follows :
1. Preparing specifications for all raw materials, packing materials, finished products, intermediates and solvents, and reagents used in analyses.
2. Inspecting, sampling, and testing of all starting materials including packaging materials, intermediate and finished products as per procedures defined in the Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
3. Performing stability testing to assess product stability.
4. Monitoring environmental conditions are met as per current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) requirements.
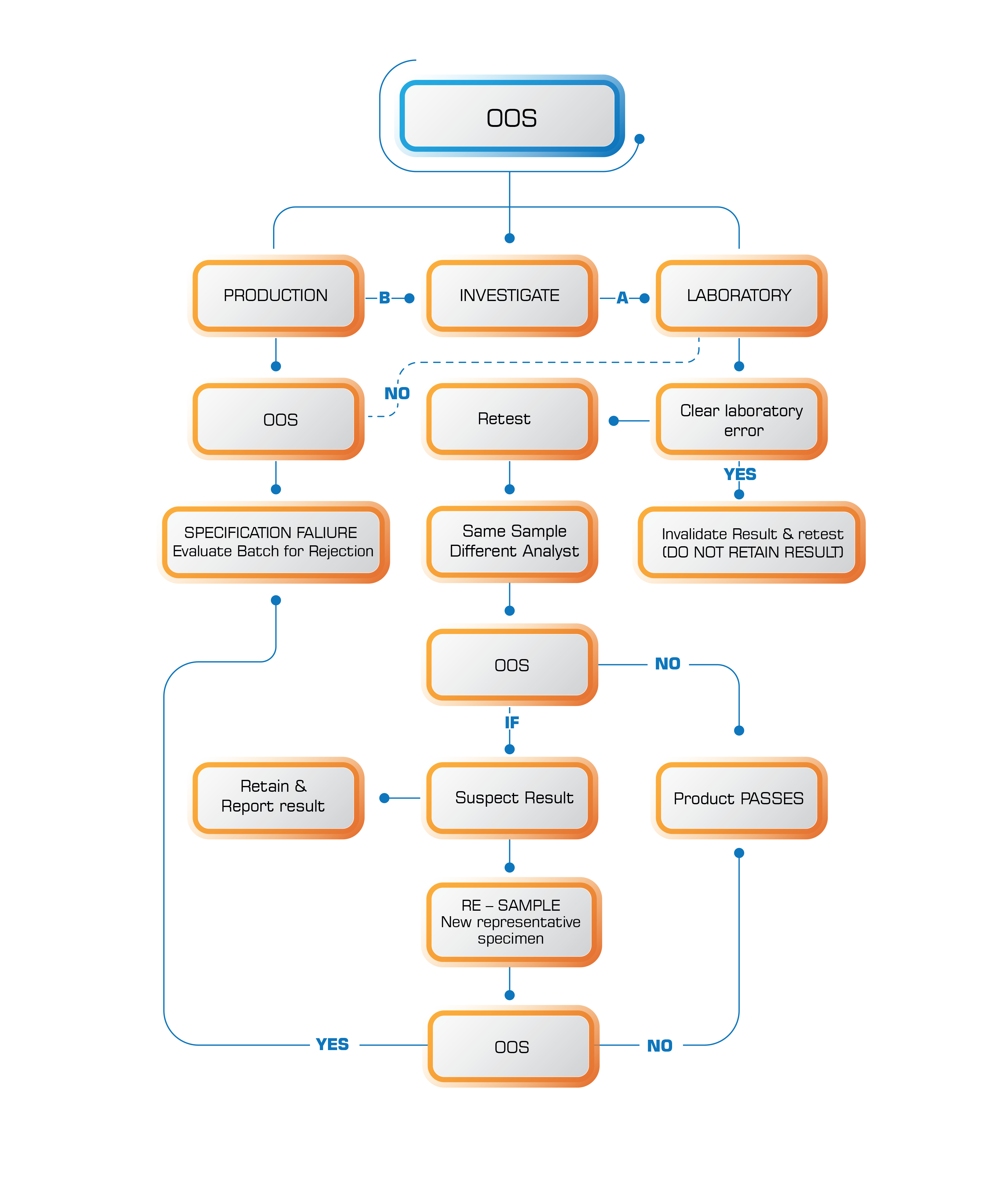
5. Preparing analysis reports for the tested samples, and recording and investigating any results that are Out Of Specifications (OOS).
6. Approving product batches for sale after ensuring it meets quality, safety and efficacy standards prescribed.
7. Calibration of all laboratory instruments and devices used in the testing.
8. Validation of analytical methods used in the testing.
9. Retaining reference samples from each batch of products released to the market.
10. Reviewing the batch manufacturing and packing records and assessing the test reports to ensure products are of the desired quality and have been properly packed and labeled.
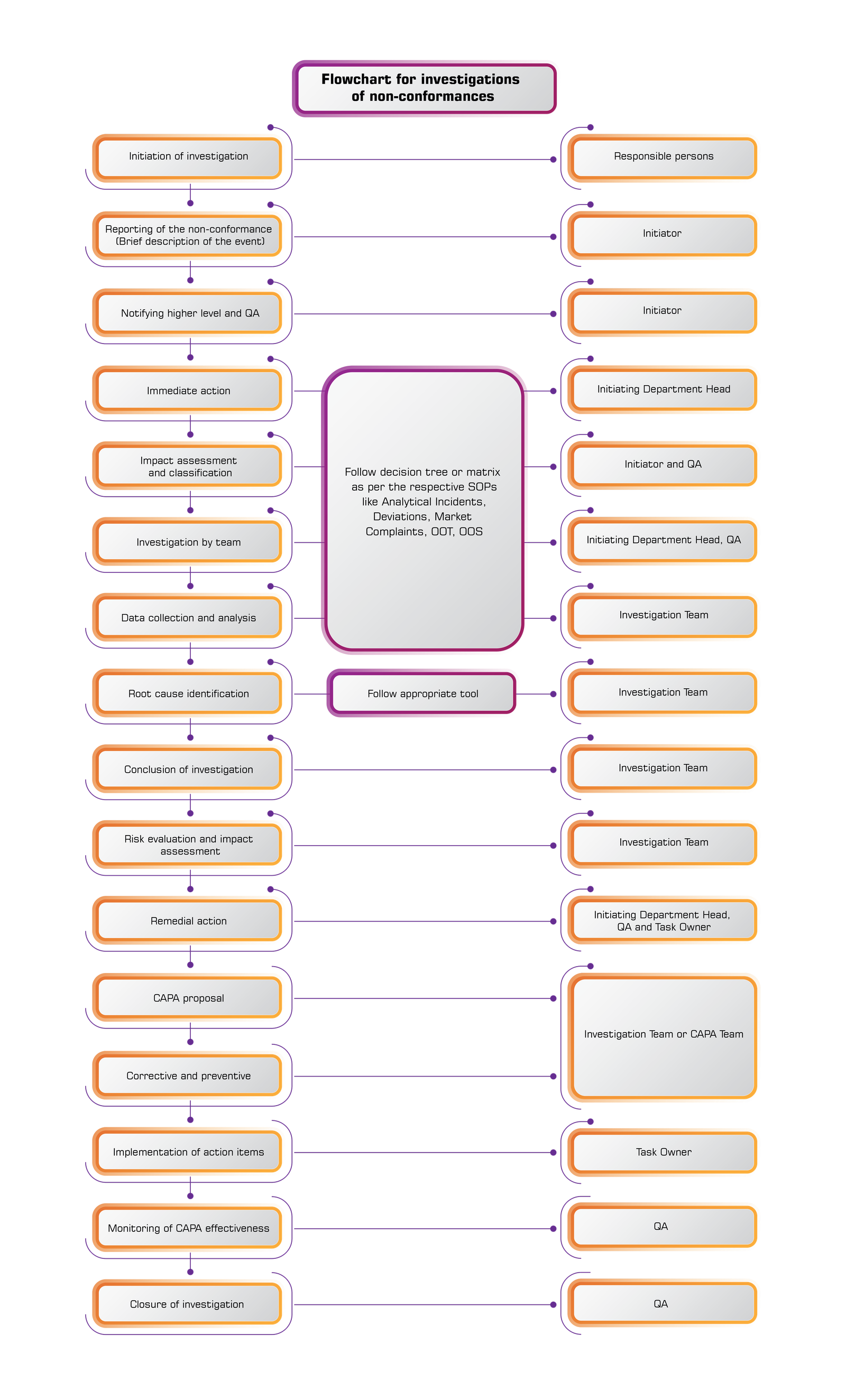
11. Participating in any investigation that follows market complaints about the quality of a product.