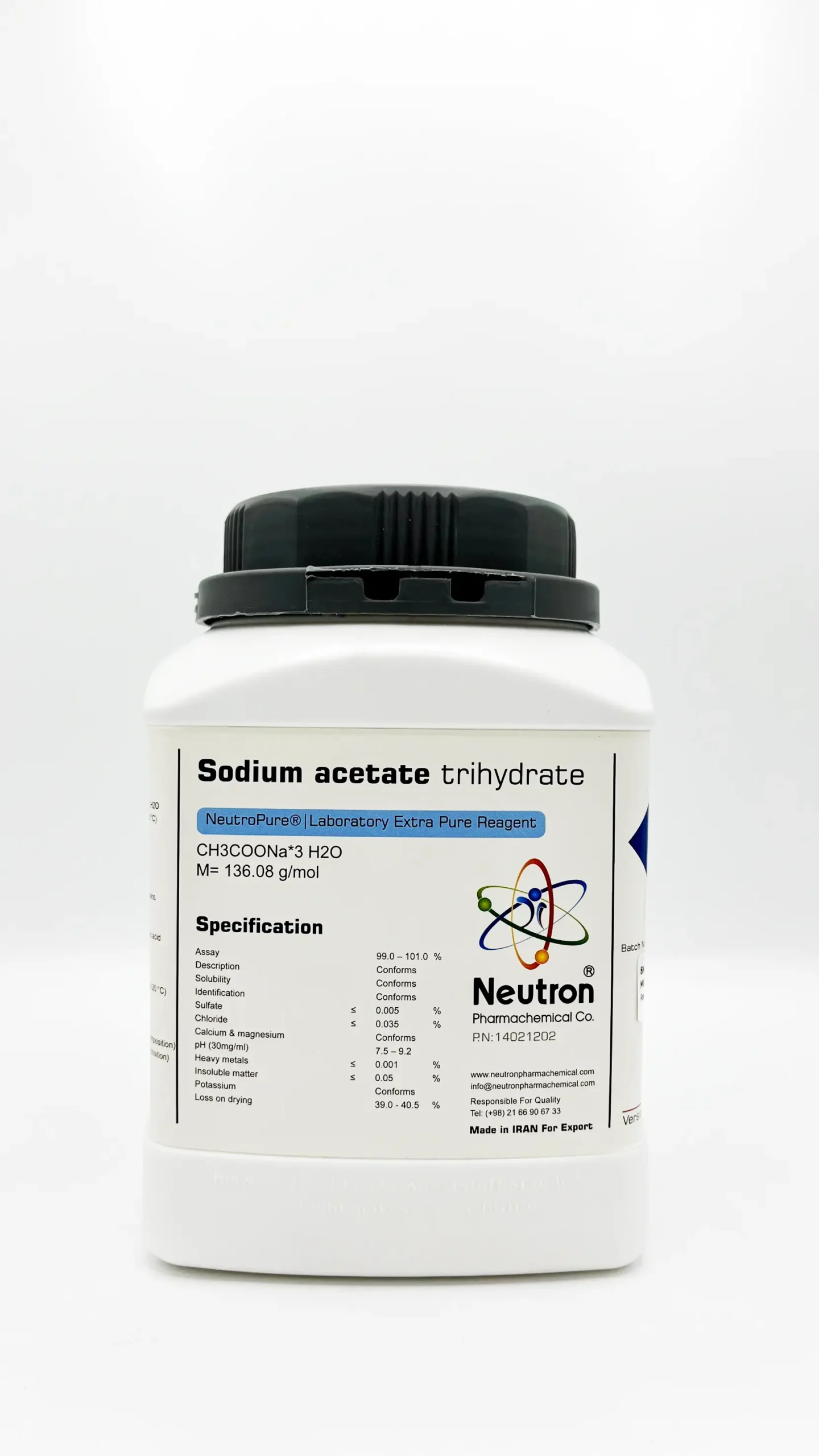
Sodium acetate trihydrate
| Formula: | C2H3NaO2 |
| Chemical formula: | CH3COONa*3 H2O |
| Density: | 1.42 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Molar mass: | 136.08 g/mol |
| Bulk density: | ~900 kg/m3 |
| CAS number: | 6131-90-4 |
| HS code: | 29152200 |
| EC number: | 204-823-8 |
| Storage (temperature): | Without limitations. |
| SDS | available |
| RTECS: | AJ4580000 |
| Odour: | weakiy of acetic acid |
| Form: | solid |
| Color: | colourless |
| Ignition temperature: | 607 °C |
| PH value: | 7.5 – 9.2 (30 g/l 20 °C) |
| Solubility in water: | 613 g/l (20°C) |
| Solubility in ethanol: | 526 g/l |
| Flash point: | > 250 °C (c.c.) |
| Boiling point: | > 400 °C (decomposition) |
| Melting point: | 324 °C (decomposition) |
| Assay | 99.0 – 101.0 | % | |
| Description | Conforms | ||
| Solubility | Conforms | ||
| Identification | Conforms | ||
| Sulfate | ≤ | 0/005 | % |
| Chloride | ≤ | 0/035 | % |
| Calcium & magnesium | Conforms | ||
| pH (30mg/ml) | 7.5 – 9.2 | ||
| Heavy metals | ≤ | 0/001 | % |
| Insoluble matter | ≤ | 0/05 | % |
| Potassium | Conforms | ||
| Loss on drying | 39.0 – 40.5 | % |
Sodium acetate trihydrate is the hydrated form of sodium acetate, an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CH₃COONa·3H₂O. It appears as a colorless or white crystalline solid and is widely used in heating pads, laboratories, and various industrial processes.
🏭⚗️ Production
Sodium acetate trihydrate is produced by reacting acetic acid with sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide, followed by crystallization from water. The resulting crystals contain three molecules of water per formula unit of sodium acetate.
🔬 Properties
Sodium acetate trihydrate is a hygroscopic, water-soluble solid with a melting point of approximately 58 °C. It is stable under normal conditions and exhibits mild alkalinity in aqueous solution. When heated above its melting point, it can undergo supercooling, which allows it to be used in reusable heat packs that crystallize upon activation, releasing stored thermal energy.
🧪 Applications
• Heat packs: Used in hand warmers and heating pads for its supercooling and exothermic crystallization properties.
• Buffering agent: Used in biochemical and pharmaceutical labs to maintain pH in various solutions.
• Food industry: Used as a preservative and flavor enhancer (E262), often in salt-and-vinegar-flavored snacks.
• Textile industry: Acts as a neutralizing agent in dyeing processes.
• Concrete and leather industries: Used to control pH and improve processing efficiency.